The most essential difference between the original copper wire and the copper-clad copper wire is the difference in the properties of the conductor material. The original copper is also called oxygen-free copper wire. It is a new copper material modified by technology. It is basically free of impurities, low in oxygen content and high in purity. It is also an ideal wire conductor material in integrated wiring. . The wire made of oxygen-free copper has low resistance, high conductivity and long transmission distance.
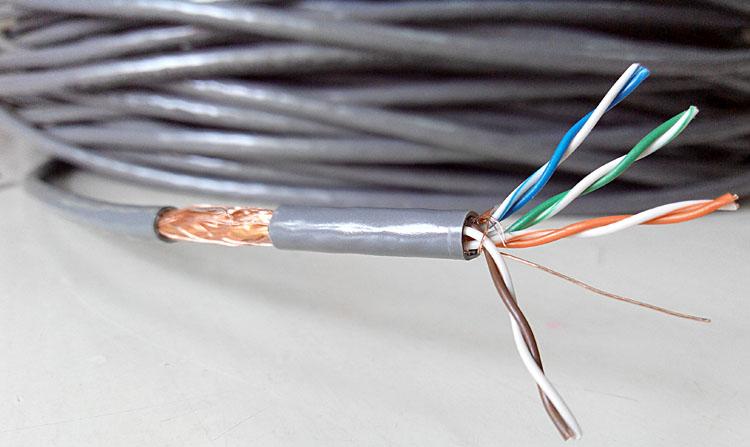
The difference between original copper and copper-clad copper wire
Copper-clad copper wire is not composed of copper. It is actually a copper wire. It is also a secondary copper. The copper-clad copper wire contains more oxides and impurities. The main cost is aluminum and the resistance is high. The transmission distance is short. The transmission quality of ordinary copper-clad copper cables within 80-100m may be affected by environmental factors, resulting in transmission instability.
Due to the skin effect in the transmission of the cable, the conductor layer of the copper-clad copper wire is coated with an oxygen-free copper to enhance the transmission performance. The purpose is to concentrate the current on the thin layer of the conductor surface when the signal is transmitted. Let this layer of oxygen-free copper enhance the quality of the transmitted signal. However, in practical applications, this approach is far less than the quality of signals transmitted directly using oxygen-free copper conductors.

Why is oxygen-free copper the most popular wire conductor material in integrated wiring? Oxygen-free copper is produced by the upper indexing method, the resistivity is about 0.0165, the oxygen content is less than 200PPM, the higher quality oxygen-free copper, and the oxygen content is as low as 100PPM. The excellent characteristics of oxygen-free copper in various aspects determine its use as a network transmission medium to better utilize cable transmission signal performance in network systems.